Lesson Plans
It all begins with an idea.
One of the main focusses of the RET program is for teachers to create 5E lesson plans that they can take back to their classrooms. Some of our RET lesson plans are featured below.
Composing Captivating Crystals
Natasja Brown & Lisa Klann
BIOLOGY
MCCRSS BIO.1B: Students will analyze the structure and function of the macromolecules that make up cells. (tie into synthetic vs. natural polymers)
CHEMISTRY
MCCRSS CHE.1.1: Use dimensional analysis (factor/label) and significant figures to convert units and solve problems.
MCCRSS CHE.1.2: Design and conduct experiments using appropriate measurements, significant figures, graphical analysis to analyze data.
PHYSICS
NGSS: HS-PS1-3: Plan and conduct an investigation to gather evidence to compare the structure of substances at the bulk scale to infer the strength of electrical forces between particles
Eggs Go Splate
Patrick Jarman
PHYSICAL SCIENCE
MCCRSS PHS.5.2: Design and conduct an investigation to study the motion of an object using properties such as displacement, time of motion, velocity, and acceleration.
MCCRSS PHS.5.3: Collect, organize, and interpret graphical data using correct metric units to determine the average speed of an object.
MCCRSS PHS.5.4: Use mathematical and computational analyses to show the relationships among force, mass, and acceleration (i.e., Newton’s second law).
MCCRSS PHS.5.7: Use mathematical and computational representations to create graphs and formulas that describe the relationships between force, work, and energy (i.e., W=Fd, KE=½ mv2 , PE=mgh, W=KE)
“Talk Curdy To Me”
Amber Riveria
BIOLOGY
MCCRSS BIO.1B: Students will analyze the structure and function of the macromolecules that make up cells.
MCCRSS BIO.1B.1: Develop and use models to compare and contrast the structure and function of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) in organisms.
MCCRSS BIO.1B.2: Design and conduct an experiment to determine how enzymes react given various environmental conditions (i.e., pH, temperature, and concentration). Analyze, interpret, graph, and present data to explain how those changing conditions affect the enzyme activity and the rate of the reactions that take place in biological organisms.
Composite Candy
Dr. Carl Dewitt & Kelvin Alford
PHYSICS
MSCCRS HS-PS2-6: Communicate scientific and technical information about why the molecular-level structure is important in the functioning of designed materials.
CHEMISTRY
MSCCRS CHE.12 : Students will understand that the bonding characteristics of carbon allow the formation of many different organic molecules with various sizes, shapes, and chemical properties.
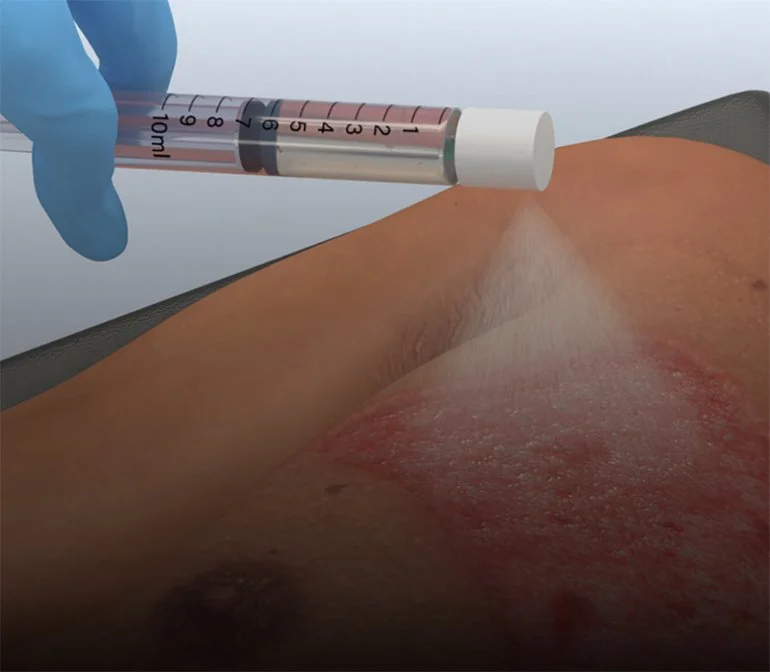
Spray on Skin
Courtney Germany
BIOLOGY
HS-LS1-2: Develop and use a model to illustrate the hierarchical organization of interacting systems that provide specific functions within multicellular organisms.
BIO.1A.3: Using specific examples, explain how cells can be organized into complex tissues, organs, and organ systems in multicellular organisms.
BIO.1E.4: Enrichment: Use an engineering design process to investigate the role of stem cells in regeneration and asexual reproduction, then develop applications of stem cell research to solve human medical conditions.
BIO.1B.1: Develop and use models to compare and contrast the structure and function of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) in organisms.
Exploring Epoxy Amine Networks, Vitrimers, and Bio-Based Polymers
Dr. Cathy Gonzalez & Tate Warren
PHYSICAL SCIENCE
MSCCRS HS.1.4: Design and conduct investigations to explore techniques in measurements of mass, volume, length, and temperature.
MSCCRS PHS.1.5: Design and conduct an investigation using graphical analysis (e.g., line graph) to determine the density of liquids and/or solids.
CHEMISTRY
MSCCRS CHE.1.2: Design and conduct experiments using appropriate measurements, significant figures, graphical analysis to analyze data.
Inkspirations a symphony of stains
Lisa Klann
PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY
MCCRSS PHY.1: Students will investigate and understand how to analyze and interpret data.
MCCRSS CHE.1.1: Use dimensional analysis (factor/label) and significant figures to convert units and solve problems.
MCCRSS CHE.1.2: Design and conduct experiments using appropriate measurements, significant figures, and graphical analysis to analyze data.
From Shrimp Tails To Food Containers
Gerrie Jones & Matthew Donaldson
MARINE & AQUATIC STUDIES
MSCCRS MAQ 4.4: Research, analyze, and communicate the effects of urbanization and continued expansion by humans on the aquatic ecosystems’ biodiversity (e.g., land use changes, erosion and sedimentation, over-fishing, invasive/exotic species, and pollution)
BIOLOGY
MSCCRS BIO 1.1: Develop and use models to compare and contrast the structure and function of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) in organisms.
Sweet Science: Exploring Properties Using Rock Science
Needra Davis-Hubbard
PHYSICAL SCIENCE
MCCRSS PHS.1: Students will demonstrate an understanding of the nature of matter.
MCRSS PHS 1.2: Use scientific research to generate models to compare physical and chemical properties of elements, compounds, and mixtures.
MCCRSS PHS 1.4: Design and conduct investigations to explore techniques in measurements of mass, volume, temperature, and length.